Kriegsspiel
Kriegsspiel is a highly accurate game of war, created by a Prussian general.
This game not only has its place in gaming history as the forerunner to modern games like Battlefield or Warhammer, but has also lead historians to the exact methods used during Prussian Warfare in the Napoleonic period.
:strip_icc()/pic1928483.jpg)
The game is directed by a combination of strategy and dice, directing pieces representing all the parts of the army during the time period. In 1862 (years after it was released in 1824) there was an update to accommodate for improved weaponry and transportation, including both railroads and telegraphs.
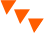
The base of many modern games, the hit point (HP), can be seen here, in the “points” that each piece is worth. The number of points relates to the number of hits each unit can take before it gets destroyed.
The game requires real-life topographical maps (a scale of 1:8000), and the tactics used reflect real-life. The use of the map itself was a show of printing and map-making technology created in the era, and with it’s rules, was used by the Prussian army as a method to teach tactics.
The goal of the game is actually determined by an umpire. the umpire also interprets the written orders (moves) of the two armies (teams of players) and is the one to move the pieces. The size of the teams is recommended to be 4-6 players each.
This does give me memories of watching a few friends of mine play Warhammer. Cheerful, pre-Covid times at game club, with the swell of voices chatting over all kinds of games.
by Abby Zarakovich





:strip_icc()/pic3436488.jpg)